射线 Ray
射线 Ray 和三维向量 Vector3 一样属于数学几何计算相关的 API,可以进行射线交叉计算。
射线 Ray
学习 Three.js 中的射线 Ray 概念,你可以类比数学几何中提到的射线,在三维空间中,一条线把一个点作为起点,然后沿着某个方向无限延伸。
// 创建射线对象Ray
const ray = new THREE.Ray();射线起点 .origin
射线 Ray 的起点 .origin 在 3D 空间中的坐标,可以用一个三维向量 Vector3 的 x、y、z 分量表示。
ray.origin = new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 3);起点 .origin 属性值是三维向量 Vector3,也可以用 .set() 方法设置。
ray.origin.set(1, 0, 3);射线方向 .direction
射线 Ray 的方向 .direction 通用用一个三维向量 Vector3 表示,向量长度保证为 1,也就是单位向量。
// 表示射线沿着x轴正方向
ray.direction = new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 0);
// 表示射线沿着x轴负方向
ray.direction = new THREE.Vector3(-1, 0, 0);
// 表示射线沿着y方向
ray.direction = new THREE.Vector3(0, 1, 0);注意 .direction 的值需要是 单位向量,不是的话可以执行 .normalize() 归一化 或者说 标准化。
ray.direction = new THREE.Vector3(5, 0, 0).normalize();// 表示射线沿着xy坐标轴的中间线
ray.direction = new THREE.Vector3(1, 1, 0).normalize();射线与三角形是否交叉 .intersectTriangle() 方法
射线 Ray 有很多关于数学计算的方法,下面就先介绍一个与三角形交叉计算相关的方法 .intersectTriangle(), 简单说,就是计算一个射线和一个三角形在 3D 空间中是否交叉。
执行 .intersectTriangle()方法,如果相交返回交点坐标,不相交返回空值 null。
// 三角形三个点坐标
const p1 = new THREE.Vector3(100, 25, 0);
const p2 = new THREE.Vector3(100, -25, 25);
const p3 = new THREE.Vector3(100, -25, -25);
//用来记录射线和三角形的交叉点
const point = new THREE.Vector3();
// `.intersectTriangle()`计算射线和三角形是否相交叉,相交返回交点,不相交返回null
const result = ray.intersectTriangle(p1, p2, p3, false, point);
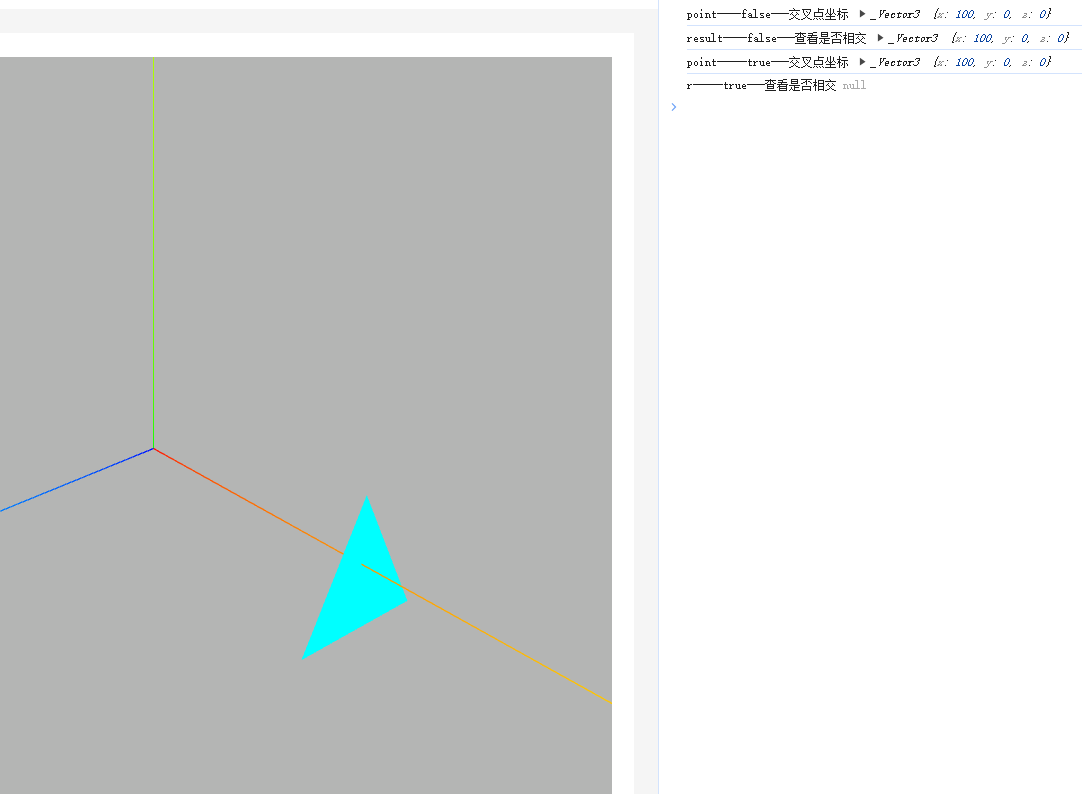
console.log("交叉点坐标", point);
console.log("查看是否相交", result);.intersectTriangle() 参数 4 表示是否进行背面剔除,p1,p2,p3 可以理解为一个三角形,有正反两面,一面是正面,一面是反面,关于三角形正反面可以参考 2.3 节讲解。
在一面观察 p1,p2,p3,如果沿着三个点的顺序转圈是逆时针方向,表示正面,另一面观察,p1,p2,p3 就是顺时针方向,表示背面。
.intersectTriangle()参数 4 设为 true,表示进行背面剔除,虽然从几何空间上讲,该案例源码射线和三角形虽然交叉,但在 threejs 中,三角形背面对着射线,视为交叉无效,进行背面剔除,返回值 r 是 null。
const r = ray.intersectTriangle(p1, p2, p3, true, point);
console.log("查看是否相交", r);示例效果如下
示例代码如下:
<template>
<div ref="raycaster"></div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue';
import * as THREE from 'three';
import model from './model.js';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js';
const raycaster = ref(null);
// 场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.add(model);
// 辅助观察坐标系
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(200);
scene.add(axesHelper);
// 灯光
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 1);
directionalLight.position.set(100, 60, 50);
scene.add(directionalLight);
// 环境光
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.4);
scene.add(ambientLight);
// 相机
const width = window.innerWidth - 296;
const height = window.innerHeight - 136;
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(30, width / height, 1, 3000);
camera.position.set(350, 250, 300);
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
// 渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true
});
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio); //防止输出模糊
renderer.setSize(width, height);
// 相机轨道控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.addEventListener('change', () => {
renderer.render(scene, camera);
});
// resize 事件会在窗口被调整大小时发生
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
const w = window.innerWidth - 296;
const h = window.innerHeight - 136;
renderer.setSize(w, h);
camera.aspect = w / h;
// 如果相机的一些属性发生了变化,需要执行 updateProjectionMatrix ()方法更新相机的投影矩阵
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
});
onMounted(() => {
renderer.setClearColor(0x444544, 0.4);
raycaster.value?.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
});
onUnmounted(() => {
renderer.dispose();
});
// 渲染循环
const render = () => {
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(render);
};
render();
</script>import * as THREE from 'three';
// 创建一个几何体对象
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
// 类型数组创建顶点数据
const vertices = new Float32Array([
100, 25, 0, // 顶点1坐标
100, -25, 25, // 顶点2坐标
100, -25, -25, // 顶点3坐标
]);
// 创建属性缓冲区对象, 3个为一组,标示一个顶点的xyz坐标
const attribue = new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3);
// 设置几何体attributes属性的位置属性
geometry.attributes.position = attribue;
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x00ffff,
side: THREE.FrontSide, // 仅正面可见
});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
// 创建射线对象ray
const ray = new THREE.Ray();
// 设置射线起点
ray.origin = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
// 设置射线方向
ray.direction = new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 0);
// 三角形三个点坐标
const p1 = new THREE.Vector3(100, 25, 0);
const p2 = new THREE.Vector3(100, -25, 25);
const p3 = new THREE.Vector3(100, -25, -25);
// point 用来记录射线和三角形的交叉点
const point = new THREE.Vector3();
const result = ray.intersectTriangle(p1, p2, p3, false, point);
console.log('point----false---交叉点坐标', point); // _Vector3 {x: 100, y: 0, z: 0}
console.log('result----false---查看是否相交', result); // _Vector3 {x: 100, y: 0, z: 0}
// 参数4 设为true 是背面剔除的意思,返回值null,返回值为null,虽然交叉,但是背面对着射线,视为无效
const r = ray.intersectTriangle(p1, p2, p3, true, point);
console.log('point-----true---交叉点坐标', point); // _Vector3 {x: 100, y: 0, z: 0}
console.log('r-----true---查看是否相交', r); // null
export default mesh;